Female hair loss
Female hair loss
Everything you need to know
Most people think that hair loss only affects men, because it often leads to baldness. However, 1 in 2 women face it, with serious psychological consequences, as hair is a key element of self-confidence and style. With early diagnosis and targeted treatments, hair loss can be treated, restoring density quickly and effectively.
Women VS Men
Although many believe that hair loss mainly affects men – as it often leads to baldness – research shows that its psychological impact is more pronounced in women.
Unlike men, women often react in the following ways:
-
They try to hide the hair loss.
-
They resort to solutions at the hair salon (new haircut, hairstyle, extensions, products for volume).
-
They invest more in the rest of their appearance (manicure, clothes, accessories) to distract attention from their hair.
As recorded in relevant studies, the phrases used by women themselves reveal intense emotional burden and low self-confidence.


Understanding Female Hair Loss
Are you noticing thinning or increased hair loss and wondering if it's more than just a seasonal change?
Hair loss affects millions of women worldwide and has a profound impact on self-confidence and mental well-being. Unlike male pattern baldness, it often occurs more slowly and gradually in women, which is why early diagnosis is crucial.
What are the causes, the most common symptoms and what are the solutions?
From specialized treatments to advanced techniques like Regrow Direct IO Hair Transplant, there are options that can restore not only your hair, but also your confidence.
What you need to know
How Does Hair Loss Appear in Women?
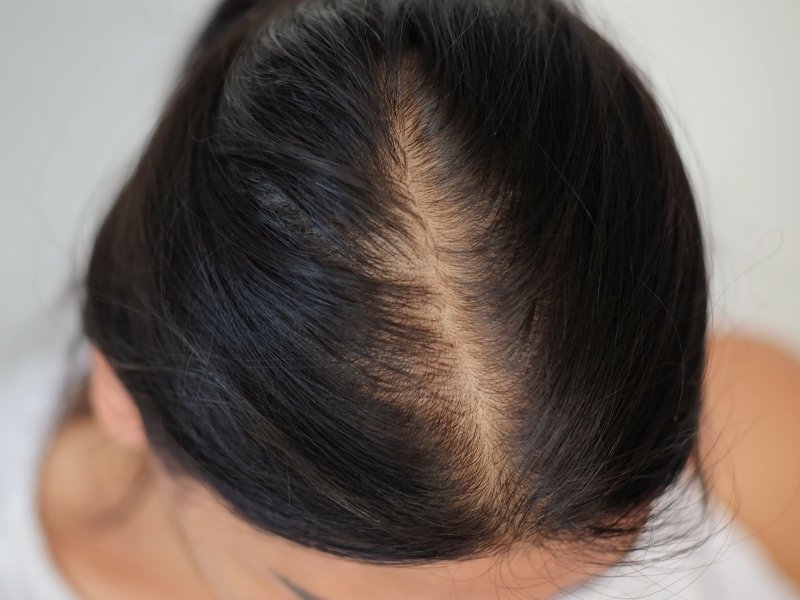
The standards hair loss in women differ significantly from male pattern baldness. While men often experience a receding hairline or bald spots on the scalp, women typically notice diffuse thinning on the crown of their head or a widening of their parting. This gradual change can be difficult to detect until a significant amount of hair has been lost.
Why is it called “Patternal Hair Loss”?
The term “standard” refers to the way in which the thinning hair follows a predictable distribution, influenced by genetic and hormonal factors. In women, the Ludwig Scale is often used to categorize the severity of hair loss.
3 signs you shouldn't ignore
The first signs of hair loss in women they often go unnoticed. Female hair loss usually progresses more slowly and in a more diffuse manner than male hair loss. In men, the most common cause of hair loss is androgenetic alopecia, or male pattern baldness, which is hereditary and mainly affects the front of the scalp, often leading to complete hair loss (baldness). Although women also suffer from androgenetic alopecia – although it is not the most common cause – they don't lose their hair to such an extent. Female hair loss is not only located in the front part of the hair, but it is diffused throughout the scalp, as a result of which it is not quickly noticed.
It has been found that by the time a woman notices that she is suffering from hair loss, 30% of hair has already been lostSo you need to be especially careful at the first symptoms:
Increased rate of hair loss
As part of the normal hair growth cycle, it is natural and expected to lose about 100-150 hairs per day. However, when the body is experiencing stress – physical or psychological – the rate of hair loss can increase to 200-225 hairs per day, which fall out when you sleep, bathe or brush your hair. Don’t underestimate this.
Reduction in hair volume
During periods of severe hair loss, hair volume is noticeably reduced. You will notice this if you try to pull your hair into a ponytail, which will be thinner. Also, the reduced hair volume makes the scalp more visible through the hair, while the parting also widens.
Change in hair texture
Hair loss can cause your hair to be thinner, break more easily, and not grow as quickly.
Types of female hair loss
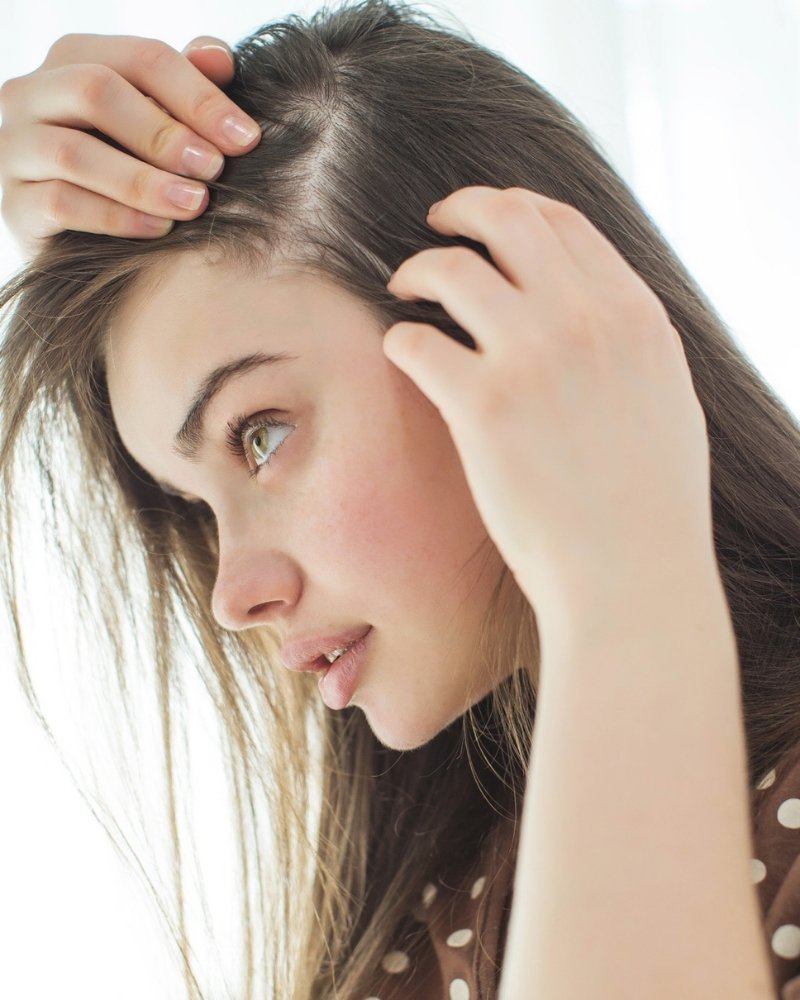

Diffuse alopecia areata
It is the most common cause of hair loss in women and occurs when a large percentage of the hair follicles on the scalp abruptly enter the telogen phase of the life cycle, which involves the shedding phase. This form of alopecia is also called telogen alopecia, precisely because it is associated with the last stage of the hair life cycle. For this premature transition of hair follicles, some external or organic stress may be responsible (e.g. sudden weight loss, pregnancy, illness, surgery, etc.) which "shocks" the growing hair follicles and puts them into a resting state earlier. The thinning of the hair is not localized to one area of the head, but is diffuse. Sometimes, it is more pronounced on the top as opposed to the sides and back of the head. However, there is no receding of the frontal line.
Women who suffer from alopecia areata never lose all of their hair, but it may be noted significant degree of dilution, and in some cases, the hair growth on the eyebrows and pubic area may also be affected. The good news is that whatever form diffuse alopecia may have, with appropriate treatment it is completely reversible. The hair follicles are not permanently affected. It is simply that more hair follicles are in the telogen phase at the same time than would be the case under normal conditions (10-20%).
Androgenetic alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia or female pattern alopecia it is hereditary and manifests itself mainly on the crown and top of the head, with the parting widening and the scalp clearly visible through the hair. This form of female hair loss often worsens as estrogen production decreases at menopause.

Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a relapsing disease that can cause hair loss anywhere on the scalp. It most commonly manifests as round or oval-shaped gaps between the hairs or even in their eyebrows. Usually, hair growth is restored after 6-12 months, but most women experience new episodes of hair loss in the same areas in the future. In some cases, alopecia areata can lead to complete hair loss (total alopecia areata). The true causes of alopecia areata areata areata areata are not known, but it is thought that it is an autoimmune disease, in which the body recognizes hair follicles as foreign and attacks them. Patients themselves usually believe that alopecia areata is triggered by intense stress and anxiety.
Traction alopecia
Traction alopecia is caused by chronic pulling (pulling) of hair follicles when a woman frequently prefers to hairstyles in which the hair is pulled in one direction (e.g. ponytails, dreadlocks, tight braids, etc.) Another form of traction alopecia is trichotillomania, which is associated with the compulsive disorder that leads some women to twirl or even pull small strands of hair, resulting in long-term gaps between their hair.

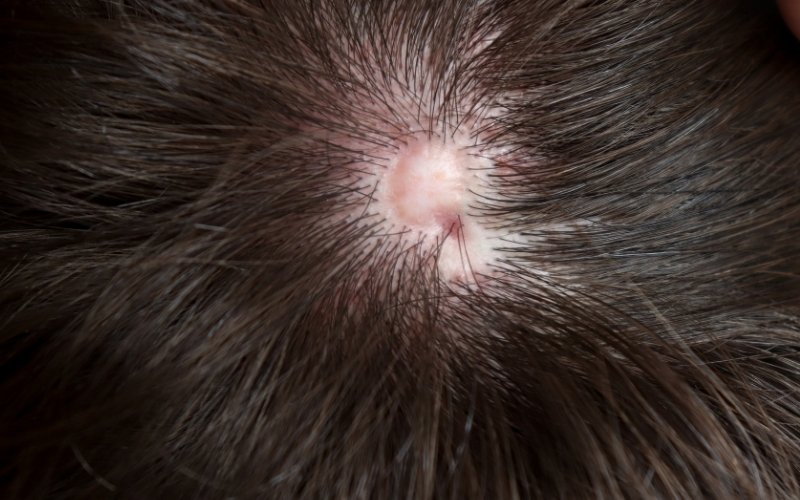
Alopecia areata
Scarring alopecia is due to a trauma or burn that has caused a permanent scar and therefore permanent hair loss in some part of the scalp. Diseases that can cause scarring alopecia are lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, but also bacterial, fungal and viral infections.
Causes of female hair loss
1: Intense stress
Chronic stress – whether physical or emotional – can trigger a response in the body that disrupts the hair life cycle. A traumatic event can also put hair follicles into a sudden resting phase.
2: Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a stressful time for the body. Most women experience significant hair loss, usually after giving birth, as hormones try to rebalance. The good news is that hair loss usually stops on its own after a few months.
3: Excessive dieting and exercise
A common cause of hair loss in young women aged 20-40 is very low-calorie diets or strict eating plans that exclude entire groups of nutrients, as well as excessive physical exercise, which cause significant strain on the body.
4: Anemia
Anemia is caused by iron deficiency, which results in a low amount of nutrients necessary to support hair growth.
5: Hypo-/Hyperthyroidism
Hair loss can be an early symptom of thyroid dysfunction and may resolve with appropriate treatment/regulation of thyroid function.
6: Polycystic ovaries
It is an endocrine disorder of the ovaries that affects approximately 101% of women of reproductive age and affects hormone levels.
7: Aggressive styling
Blonde dyes, perms, blow dryers, straighteners, and excessive styling damage the hair.
8: Low-protein diet
Proteins are the building blocks of hair. If you reduce the amount of protein in your diet, it is possible that the hair life cycle will be affected.

Hair loss during pregnancy
Hair loss can occur either during or after pregnancy, adding another source of concern for new mothers. The good news is that this type of hair loss is very common and usually only temporary. However, there is an important distinction to make. If it occurs during pregnancy, then it can be a sign of a hormonal imbalance or nutritional deficiency. Usually, hair loss occurs after childbirth (postpartum hair loss) and is due to two factors: hormones and stress.
During pregnancy, hormone levels change, most notably a rapid increase in estrogen production. Immediately after childbirth, however, estrogen levels drop dramatically, which can be accompanied by severe hair loss. In addition, many women start taking birth control pills, which are likely to cause further hormonal fluctuations and worsen the phenomenon of hair loss. At the same time, the stress, the sleepless nights and the new responsibilities that motherhood entails, constitute a state of intense stress for the body that can lead to hair loss.
Hair loss during menopause
During menopause, you may notice hair growth in places where you didn't have it before (hirsutism), or see: your hair thinning and becoming weaker and more limp. The main cause is the changes in hormone levels during this period. Estrogen and progesterone levels drop, causing androgen (male hormone) levels to rise. At the same time, if you suffer from androgenetic alopecia, you may experience a worsening, as this form of hair loss is affected by hormonal changes. During and after menopause, hair can become thinner as hair follicles shrink, hair growth slows down, and hair loss becomes more severe.
Ludwig scale
The Ludwig scale is a globally recognized grading system for female hair loss. Based on the Ludwig scale, there are three stages of hair loss.
Type I
The thinning begins at the top of the head or around the crown. This type is quite mild and goes almost unnoticed. Some women are able to recognize the first signs of thinning at this stage by carefully observing their parting as it begins to widen. However, many times the thinning is not noticed because in female pattern hair loss, hair is not lost only from the front area, as is the case with male pattern hair loss, but from the entire head.
Type II
In the second type, hair thinning is more noticeable, mainly on the top of the head and the crown. The hair is thinner and sparser, while hair loss is also more pronounced. In addition, styling the hair is more demanding, as some of its volume has been lost and the parting has become wider.
Type III
It is the most advanced stage of female pattern hair loss. The scalp is clearly visible, as the hair has thinned and thinned to such an extent that it cannot be hidden. This is the stage that cases of androgenetic alopecia usually reach, while in contrast to other forms of hair loss there is a milder thinning of the hair.
Treatment of female hair loss
In order to formulate the appropriate treatment plan, it is important to first investigate the true cause of hair loss.
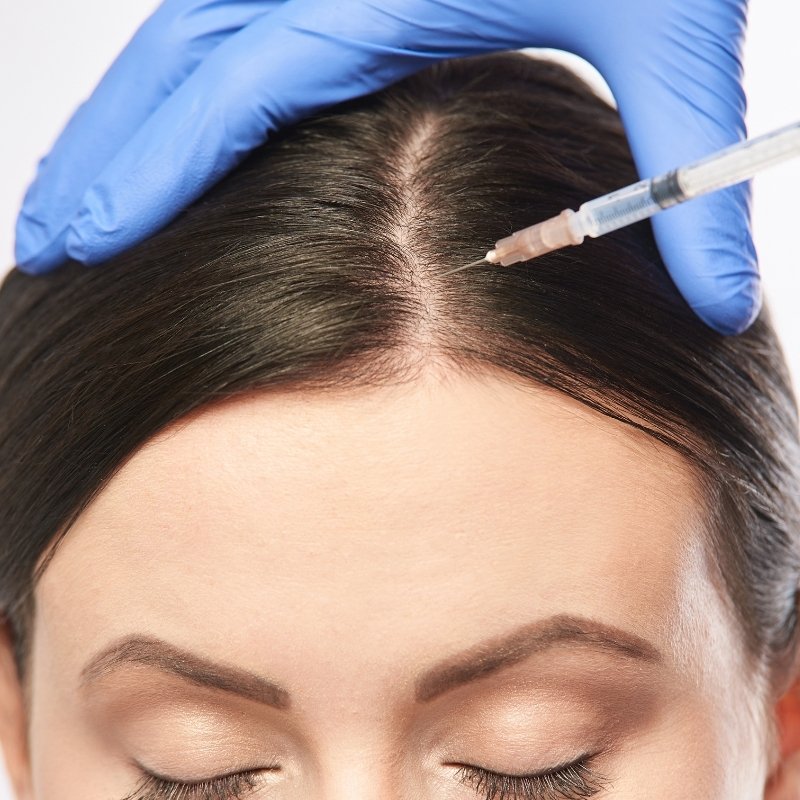
Modern treatments stop hair loss and restore hair density
For an early diagnosis, we take a complete medical history and apply detailed trichoscopy to record the density and characteristics in detail of your hair, as well and the degree of hair lossAlso, for a correct and complete diagnosis, you may be asked for some blood or hormonal tests.
Once the cause and degree of hair loss are determined, a personalized treatment plan is formulated that may include conservative treatment of hair loss with: medication and strengthening hair growth with autologous PRP mesotherapy or, if the conditions are met, to propose a definitive treatment of the thinning with the minimally invasive method of hair transplantThere is also the technique Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) that can provide a hair density effect with the painless and safe method of medical tattooing on the scalp.





